Blood Formation | Function | Types
Blood Formation | Function | Types
Blood
- Blood is a liquid connective tissue.
- It is fluid of growth.
- the fluid of health the body.
 |
| Blood Formation | Function | Types |
Properties of blood
- Colour: Blood is Red in color, (Haemoglobin)
- Total volume: 6-7 liter (8%) in a normal young healthy adult weighing about 70 kg
- PH 7.4 (Alkaline)
- Specific Gravity: 1.050- 1.060
Composition of Blood
Blood is two types of plasma or cells
- Cells 45% (RBC, WBC. Platelets)
- Plasma 55%. (Protein, water, other)
Plasma protein (Albumin, Globulin, fibrinogen)
Plasma
- Plasma is clear.
- Plasma is a major part of blood.
- The total blood volume of blood in plasma is 55%
Plasma composition
Functions of plasma proteins:
- Helps in the coagulation of blood.
- Helps in the maintenance of osmatic
- Helps in pressure in the blood.
- Helps in transport and reservoir.
- Helps in maintenance viscosity of blood
- Helps in the maintenance system of blood.
- Helps in the maintenance of acid-base balance.
- Immune System
Blood Cells
They are three types
- RBC - WBC - Platelets
RBC (Red blood cells) / erythrocytes.
- It is non-nucleated
- It is also known as Erythrocytes
- The red color of RBC is because of the presence of hemoglobin.
- It is an important role of transport of gases.
Normal Range of RBC- 4 to 5.5 million / cumion of blood
- Male 4.5-5.5 million/ cumm
- Female 4- 4.5 million /cumm
Properties of RBC
- Rouleaux formation
- PCV
- Suspension stability.
Function of RBC
- Transport of or from the lungs to the tissues.
- Transport of co₂ from the tissues to the lungs
- Buffering Action in blood.
- It helps in blood Group determination.
WBC (White Blood Cells) / Leukocytes
- Nucleated formed
- colorless
- Compared to RBC, the WBC are large in size and lesser in number.
Normal range of WBC -4000-1100/cumm of blood
WBC types:
On the basis of granules
Granulocyte
- Neutrophil
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
Agranulocyte
- Monocyte
- Lymphocyte
NEUTROPHIL (50-70%)
 |
| NEUTROPHIL (50-70%) |
Cell Size:10-14 um
Nucleus: Multi-lobed (1-6 lobes), purple in color
Cytoplasm: Slight bluish
Granules: Fine, sand-like particles, red-brown or purplish in color
Function: Phagocytosis, mediate the febrile response
EOSINOPHIL (1-4 %)
 |
| EOSINOPHIL (1-4 %) |
Cell Size: 10-14 um
Nucleus; Bi-lobed, spectacle shape, purple in color
Cytoplasm: Eosinophilic, light pink in color
Granules: Large, coarse, brick red in color, do not cover the nucleus
Function: Mild Phagocytosis, limiting Allergic manifestations, provide local mucosal immunity
BASOPHIL (<1 %)
 |
| BASOPHIL (<1 %) |
Cell Size: 10-14 um
Nucleus: Bi-lobed, purple in color, arranges in shape
Cytoplasm: Basophilic, Blue in appearance
Granules: purple R Large, coarse, purple/blue, overlying nucleus
Function: Mild Phagocytosis, Allergic manifestations
MONOCYTE (2-8%)
 |
| MONOCYTE (2-8%) |
Cell Size:10-18 μm
Nucleus: Single, kidney shape, pale in color, peripheral in position
Cytoplasm: Phagocytosis, work as tissue macrophages
Granules: Pale blue, amount more than the nucleus HAR
Function :Absent
LYMPHOCYTE (20-40 %)
 |
| LYMPHOCYTE (20-40 %) |
Cell size: 7-10 µm (equal to RBC size) LL: 10-14 um (double to RBC size)
Nucleus: Single, very big, oval/round in shape, central in position, occupying whole of the cell
Cytoplasm: Scanty, sky blue in color, less amount than a nucleus
Granules: Absent
Function: Produce antibodies
Properties of each WBC
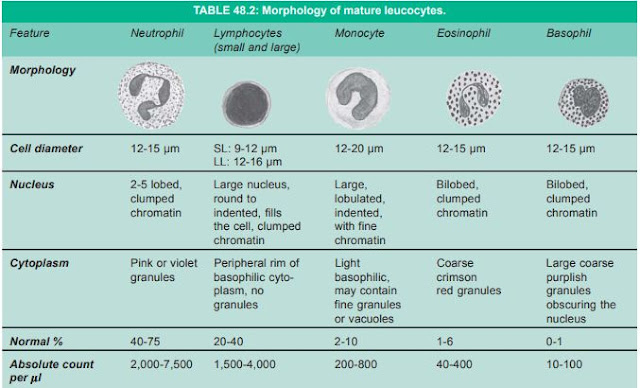 |
Absolute value
Polymorphs(P) 40-75% 2,000-7,500/µl
Lymphocytes(L) 20-40% 1,500-4,000/µl
Monocytes(M) 2-10% 200-800/µl
Eosinophils(E) 1-6% 40-400/µl
Basophils(B) 0-1% 10-100/µ
Platelets / Thrombocytes :
- Non- Nucleated
- Size of platelets 2.54
- Volume 7.5cuu
- The shape of platelets: Oval disk, dumb-bell shape, Comma shape, cigar shape rod.
Normal Range $1.5-4.5 Lac/cum
The function of platelets
- Blood clotting
- Blood loss
- PDGF Repairs
- Defense mechanism
- Role in clot Retraction
The function of Blood:
- Respiratory function
- Excretory function
- transport of Hormones and Enzymes
- Regulation of water balance
- Regulation of Acid-base balance
- Regulation of body temperature.
- storage function Defensive function...
- Production of Energy.